Temporarily disabling caching
- English
- 日本語
Caching can be disabled:
- at the individual URL level,
- at the browser level, and
- at the site level.
Disabling caching at the individual URL level
- Log in to the Fastly control panel.
- From the Home page, select the appropriate service. You can use the search box to search by ID, name, or domain.
- Click Edit configuration and then select the option to clone the active version.
- Click Settings.
Click Create cache setting to create a new cache setting.
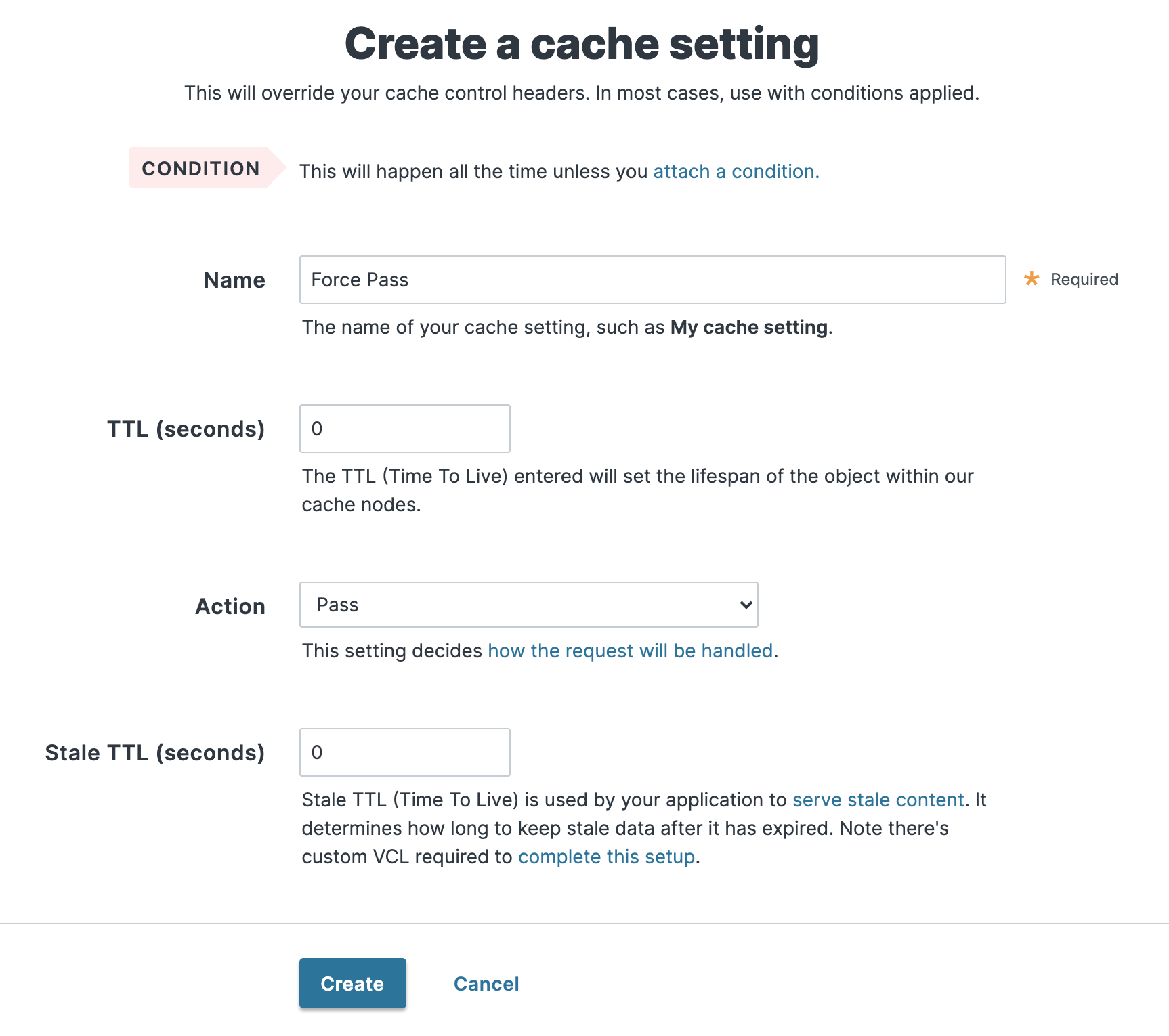
Fill out the Create a cache setting fields as follows:
- In the Name field, enter a descriptive name for the new cache setting (e.g.,
Force Pass). - In the TTL (seconds) field, enter
0to set the lifespan of the object in our cache nodes to zero. - From the Action menu, select Pass (do not cache) to pass the request and avoid caching it.
- In the Stale TTL (seconds) field, enter
0to set the amount of time to serve stale content, in seconds, to zero.
- In the Name field, enter a descriptive name for the new cache setting (e.g.,
Click Create.
Click the Attach a condition link to the right of the newly created cache setting.
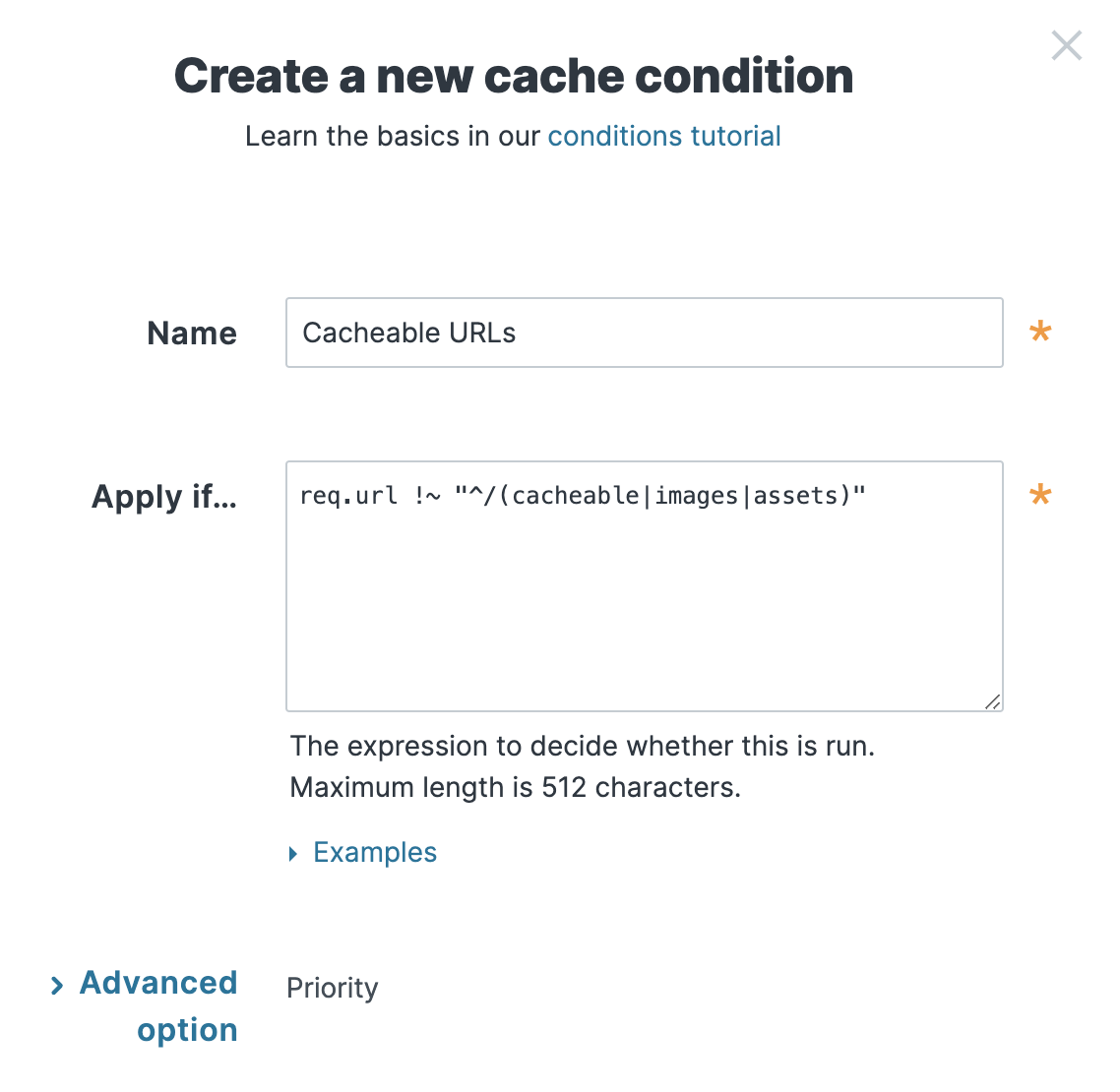
Fill out the Create a new cache condition fields as follows:
- In the Name field, enter a descriptive name for the condition (e.g.,
Cacheable URLs). - In the Apply if field, create a condition that matches the URLs to not cache. For example, you could enter
req.url !~ "^/(cacheable|images|assets)"to set the condition to look for URLs that do not start with/cacheable,/images, or/assets. If the condition finds them, the URLs should be cached. If the condition doesn't find them, the cache setting that is set toPassensures the URLs are explicitly not cached.
- In the Name field, enter a descriptive name for the condition (e.g.,
Click Save and apply to.
- From the Activate menu, select Activate on Production to deploy your configuration changes.
HINT: You can use these steps to override default caching based on a backend response.
Disabling caching at the browser level
Theoretically, all browsers should follow the stated rules of the HTTP standard. In practice, however, some browsers don't strictly follow these rules. The following combination of headers seems to force absolutely no caching with every browser we've tested.
Cache-Control: no-cache, no-store, private, must-revalidate, max-age=0, max-stale=0, post-check=0, pre-check=0Pragma: no-cacheExpires: 0WARNING: If you want your content cached in Fastly but not cached on the browser, you must not add these headers on your origin server. Instead, add these as new Headers on the Content page and be sure the Type is set to Response.
Disabling caching at the site level
You can disable caching at the site level by creating a VCL Snippet to pass on all requests to your service:
- Log in to the Fastly control panel.
- From the Home page, select the appropriate service. You can use the search box to search by ID, name, or domain.
- Click Edit configuration and then select the option to clone the active version.
Click VCL.
Click VCL snippets.
Click Add snippet.
Fill out the Add VCL snippet fields as follows:
- Using the Type controls, select Regular to create a regular VCL snippet.
- In the Name field, enter an appropriate name (e.g.,
Pass All Requests). - Using the Placement controls, select Within subroutine.
- From the Subroutine menu, select recv (
vcl_recv). - (Optional) In the Priority field, enter the order in which you want the snippet to execute. Lower numbers execute first.
- In the VCL editor, add the following code:
return(pass);Click Add to create the snippet.
- From the Activate menu, select Activate on Production to deploy your configuration changes.
All requests will continue to be passed until you remove return(pass); from vcl_recv in your VCL or you delete this snippet.